Lung Cancer Detection
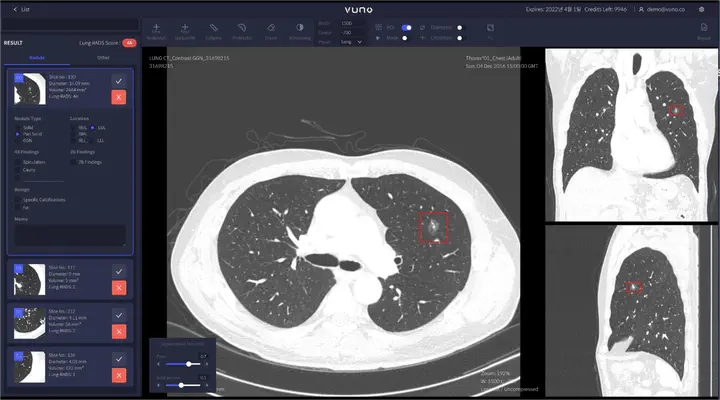 photo from https://www.vuno.co/lung
photo from https://www.vuno.co/lungObjective ⛳️
Development of a solution for early detection and analysis of nodules that can develop into lung cancer from lung CT scan information of patients.
Data 📝
Description
- About 1,000 scans from anonymous hospitals in the United States, Korea, and Japan (Private dataset)
- LUNA16 (Public dataset)
Preprocess
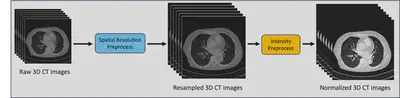
- Since the spacing resolutions of individual raw 3D CT images are different, all CT images are resampled to the target spacing. (Spatial Resolution Preprocessing)
- The resampled CT images are windowed and normalized from the Hounsfield Unit (HU) value. (Intensity Preprocessing)
Annotation
- Nodule coordinates and size (x, y, z, d)
- Consensus score (number of radiologists who agree out of 4)
Challeges 🤔
- The ambiguity of the criteria for defining a nodule among radiologists.
- The location of nodules is annotated in 3D CT, but information about non-nodules is insufficient.
- Nodules are relatively small and rare compared to the size of a 3D CT volume.
Method 💡

Detection Nodule Candidates (1 stage)
- The problem is viewed from the scan level to the patch level by applying the sliding window method to the pre-processed 3D CT images.
- During training, patches that contain annotated nodules are used to train the detection network.
- Since the volume size of the nodule varies greatly, 3D modeling is performed considering multi-scale features.
- Network composition: backbone, neck, head (Similar to CenterNet)
- Input: 3D patch, 3D heatmap
- Output: Output heatmap
- Consensus information is reflected in the loss function.
- Duplicate predictions are removed through volumetric NMS.
- Evaluation and Analysis
- Optimization and encryption through torchscipt
- Deploy
Candidate Scoring Network (2 stage)
- Utilize the nodule candidate patch from the detector as inputs.
- Generates negative nodule patches for training.
- Uses test-time augmentation (TTA) to improve the recall for small nodules.
- Evaluation and Analysis
- Optimization and encryption through torchscipt
- Deploy